使用SomaticSignatures进行突变数据的signature的判断
SomaticSignatures包于2015年发表在bioinformatcis杂志上,该杂志为专业的生物信息学杂志,该包旨在通过对肿瘤的single-nucleotide variants(SNP)数据进行分析,找到肿瘤发生发展,演化机制。本文将介绍如何使用snv数据分析得到该肿瘤的特征snp。
数据准备
数据需要的是SNP数据,其中需要的数据有"Sample",“chr”, “pos”,“ref”, “alt”,分别为样本,染色体,snp起始位置,结束位置,参考ref的碱基,alt的碱基。对于下载到的TCGA的数据,我还是使用python处理好。 原始数据
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("TCGA.CRC.mutect.maf.csv")
df.head()
"""
Hugo_Symbol Entrez_Gene_Id ... MC3_Overlap GDC_Validation_Status
0 UBE2J2 118424 ... True Unknown
1 RPL22 6146 ... True Unknown
2 TNFRSF9 3604 ... True Unknown
3 EXOSC10 5394 ... False Unknown
4 PTCHD2 57540 ... True Unknown
"""
df = df[df.Variant_Type=='SNP']
#首先筛选snp数据
newdf = df.iloc[:,[33,4,5,11,12]]
#挑选特定列
newdf.columns = ["Sample","chr", "start","ref", "alt"]
newdf.ref = newdf.ref.str[:1]
# 去除ref与alt一样的行,否则后续会出错
newdf = newdf[newdf.ref != newdf.alt]
#保存数据用于R分析
newdf.to_csv("TCGA.CRC.mutect.maf.filtered.csv",index=None)
筛选Signatures
这里采用R来进行分析,以为要使用到SomaticSignatures包,首先安装必要的包
install.packages(c("SomaticSignatures","SomaticCancerAlterations","BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg38","data.table"))
导入包
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(SomaticSignatures))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(SomaticCancerAlterations))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg38))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(data.table))
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(ggplot2))
读入数据并将数据导入成mutationContext需要的数据
df=fread('TCGA.CRC.mutect.maf.filtered.csv',data.table = F)
# ["Sample","chr", "start","end","ref", "alt"]
alls=as.character(unique(df$Sample))
df$study=df$Sample
sca_vr = VRanges(
seqnames = df$chr ,
ranges = IRanges(start = df$start,end = df$start+1),
ref = df$ref,
alt = df$alt,
sampleNames = as.character(df$Sample),
study=as.character(df$study))
运行mutationContext并将signature画出来并检查其表达的方差
sca_motifs = mutationContext(sca_vr, BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg38)
head(sca_motifs)
# 对每个样本,计算 96 突变可能性的 比例分布情况
escc_sca_mm = motifMatrix(sca_motifs, group = "study", normalize = TRUE)
dim( escc_sca_mm )
table(colSums(escc_sca_mm))
head(escc_sca_mm[,1:4])
n_sigs = 5:15
gof_nmf = assessNumberSignatures(escc_sca_mm , n_sigs, nReplicates = 5)
save(gof_nmf,file = 'gof_nmf.Rdata')
load(file = 'gof_nmf.Rdata')
# 这个 assessNumberSignatures 步骤耗时很严重。
pdf("plotNumberSignatures.pdf",width=18, height=7)
plotNumberSignatures(gof_nmf)
dev.off()
结果显示
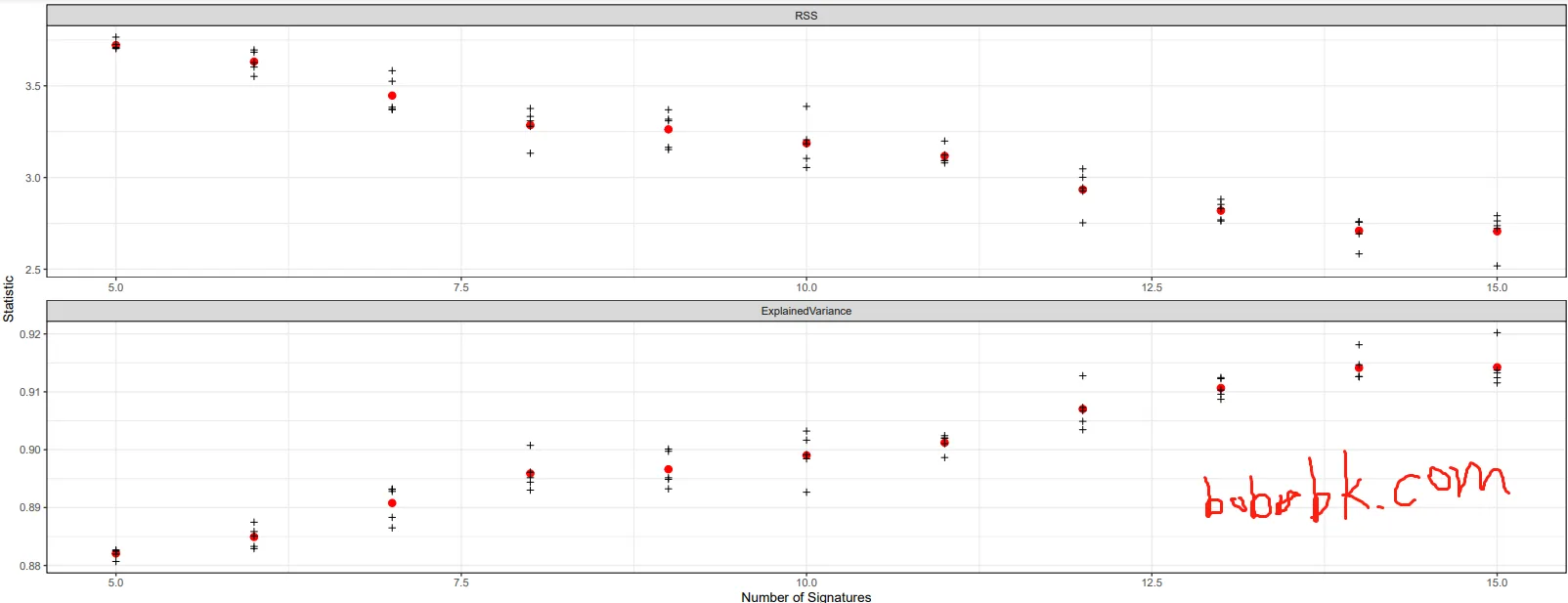 当signature达到13时便差不多到达99%的方差了
当signature达到13时便差不多到达99%的方差了
signature的绘制
最后我们通过前一步筛选的somatic muatiaon的signature
sigs_nmf = identifySignatures(escc_sca_mm ,
11, nmfDecomposition)
save(escc_sca_mm,sigs_nmf,file = 'escc_denovo_results.Rata')
load(file = 'escc_denovo_results.Rata')
str(sigs_nmf)
library(ggplot2)
pdf("maf.pdf",width=18, height=7)
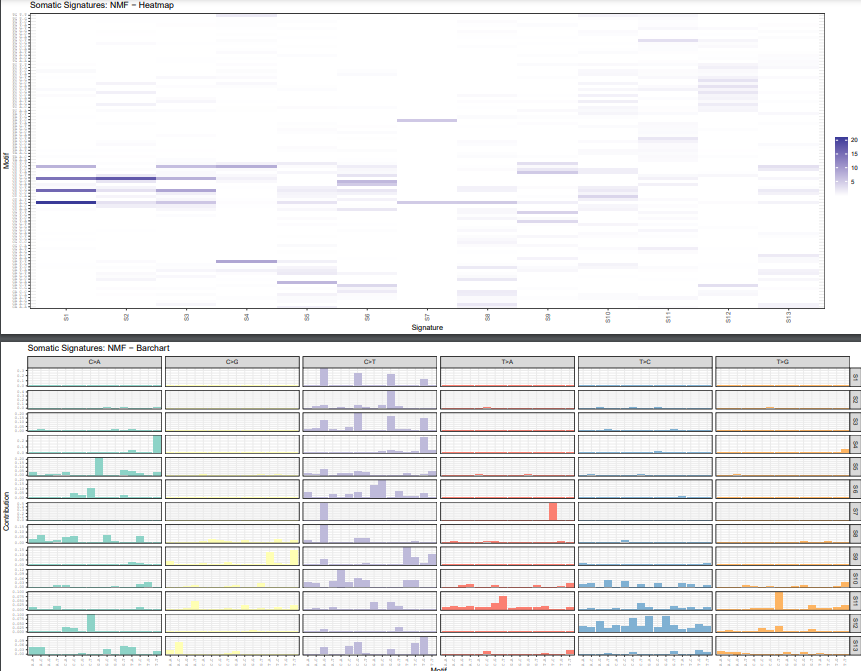
plotSignatureMap(sigs_nmf) + ggtitle("Somatic Signatures: NMF - Heatmap")
plotSignatures(sigs_nmf, normalize =T) +
ggtitle("Somatic Signatures: NMF - Barchart") +
facet_grid(signature ~ alteration,scales = "free_y")
dev.off()
最后结果
总结
本文用于在肿瘤数据中筛选出需要的signature的snp(可以使用病人数据或者TCGA公共数据),而不是采用cosmic数据库的30个肿瘤突变signature,对于特定肿瘤方面的专家可以找到更d意d的结果。
- 原文作者:春江暮客
- 原文链接:https://www.bobobk.com/871.html
- 版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可,非商业转载请注明出处(作者,原文链接),商业转载请联系作者获得授权。